해당 링크를 참고하여 공부한 내용을 정리합니다.
PyTorch에서의 Tensor는 Torch의 것과 거의 동일하게 동작함
import torch
#초기화되지 않은 (5x7) 크기의 tensor를 생성함.
a = torch.empty(5, 7, dtype = torch.float)
평균 0, 분산 1의 정규분포를 따르는 무작위 숫자로 double tensor를 초기화 함.
a = torch.randn(5, 7, dtype = torch.double)
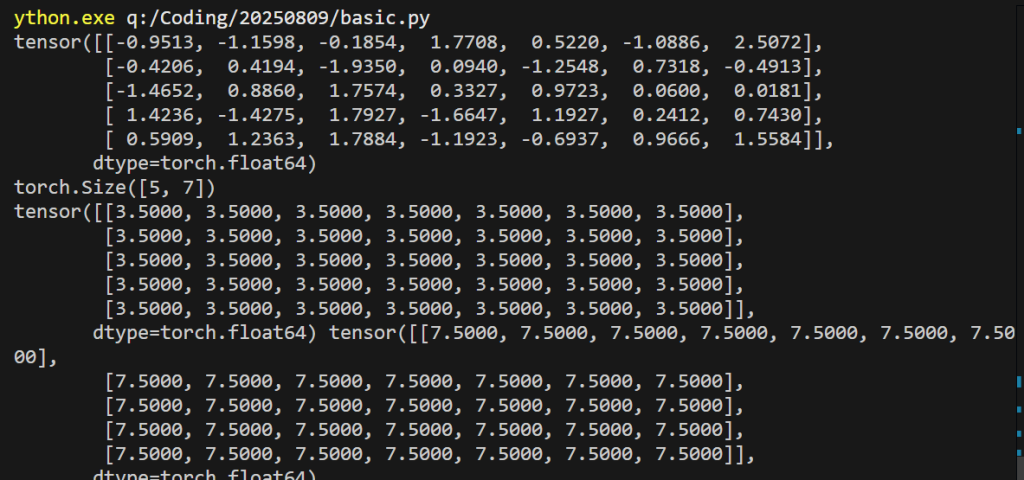
print(a)
print(a.size())

a.fill_(3.5)
#a가 값 3.5로 채워짐
b = a.add(4.0)
# a는 여전히 3.5이다.
#3.5 + 4.0 = 7.5의 값이 반환되어서 새로운 tensor b가 됨.
print(a, b)
IN-PLACE/OUT-OF-PlACE
첫 번째 차이점은 tensor의 모든 In-place 연산은 _ 접미사를 갖는다는 것이다. 예를 들어, add는 연산 결과를 돌려주는 Out-of-place 연산을 하고, add_는 In-place 연산을 함.
import torch
#초기화되지 않은 (5x7) 크기의 tensor를 생성함.
a = torch.empty(5, 7, dtype = torch.float)
a = torch.randn(5, 7, dtype = torch.double)
print(a)
print(a.size())
a.fill_(3.5)
#a가 값 3.5로 채워짐
b = a.add(4.0)
# a는 여전히 3.5이다.
#3.5 + 4.0 = 7.5의 값이 반환되어서 새로운 tensor b가 됨.
print(a, b)
a.fill_(3.5)
#a가 3.5로 채워짐
b = a.add(4.0)
#a는 여전히 3.5이다.
#3.5 + 4.0 = 7.5의 값이 반환되어 새로운 tensor b가 됨.
print(a,b)
c = a.add_(10)
print(c)0-인덱스(ZERO INDEXING)
또 다른 차이점은 Tensor의 인덱스는 0부터 시작(0-인덱스)라는 점이다. (Lua에서 tensor는 1-인덱스를 갖는다.)
b = a[0,3] #select 1st row, 4th column from a
Python의 슬라이싱(slicing)으로도 Tensor를 인덱스 할 수 있다.