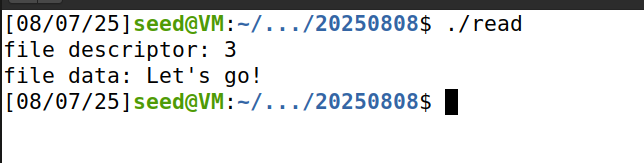
이번에는 지난번에 생성한 data*.txt파일 들을 read함수를 이용해서 읽어 들인다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define BUF_SIZE 100
void error_handling(char * message);
int main(void)
{
int fd;
char buf[BUF_SIZE];
fd = open("data2.txt" , O_RDONLY);
if(fd == -1)
error_handling("open() error!");
printf("file descriptor: %d \n", fd);
if(read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf)) == -1)
error_handling("read() error!");
printf("file data: %s", buf);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
void error_handling(char* message)
{
fputs(message, stderr);
fputc('\n', stderr);
exit(1);
}
다음과 같은 코드를 사용하여 파일에 적힌 내용을 출력할 수 있었다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
int main(void)
{
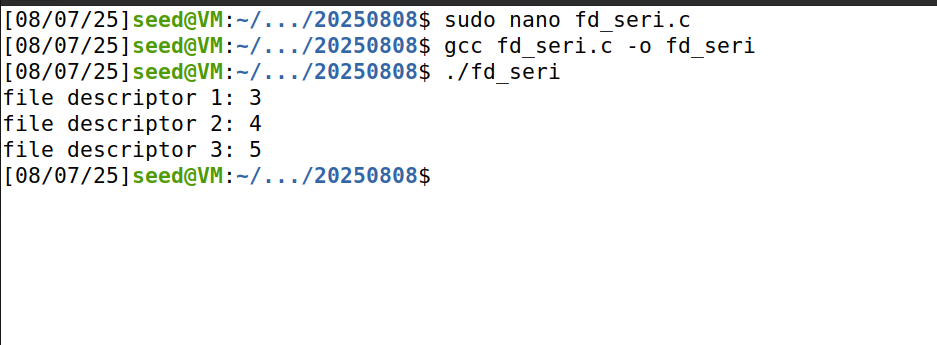
int fd1, fd2, fd3;
fd1 = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
fd2 = open("test.dat", O_CREAT|O_WRONLY|O_TRUNC);
fd3 = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
printf("file descriptor 1: %d\n", fd1);
printf("file descriptor 2: %d\n", fd2);
printf("file descriptor 3: %d\n", fd3);
close(fd1); close(fd2); close(fd3);
return 0;
}
WORD 는 unsigned short로 정의되어 있음